Essential Guide to Photovoltaic System Design Strategies
Comprehensive Guide to Photovoltaic System Design
Photovoltaic system design is a crucial aspect of harnessing solar energy efficiently and effectively. As the demand for renewable energy sources grows, understanding the principles behind designing these systems becomes essential for homeowners, businesses, and industries alike. This article delves into the intricacies of photovoltaic system design, covering the fundamental concepts, systems principles, inverter roles, installation best practices, financial considerations, and future trends in technology.
The essence of photovoltaic system design lies not only in selecting the right components but also in ensuring that the system meets the specific energy needs of the user while being cost-effective. This involves assessing various factors such as location, energy consumption patterns, system size requirements, and potential incentives that encourage the transition to solar energy. Transitioning to solar energy through thoughtful photovoltaic system design contributes significantly to sustainability and energy independence.
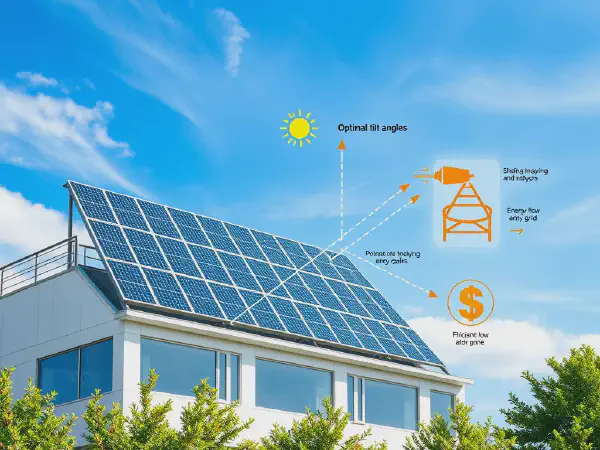
In implementing a photovoltaic system, one must consider variables such as the orientation and tilt of solar panels, shading effects, and the reliability of the grid connection. Each design decision impacts overall system performance, efficiency, and return on investment. Successful photovoltaic system design requires a systematic approach that combines hardware, software, and engineering principles to create a reliable and sustainable energy generation solution.
As technology advances, it is essential to stay updated on the latest developments in photovoltaic systems. Innovations in solar panel efficiency, inverter technology, and integration with energy storage solutions have transformed how photovoltaic systems are designed and deployed. These advancements allow for greater flexibility and efficiency in energy generation, making solar power more accessible to a broader range of users.
In summary, photovoltaic system design encompasses a wide array of considerations, from technical specifications to financial viability. A thorough understanding of system components, design principles, installation best practices, financial incentives, and future technology trends will enable designers to create optimized photovoltaic systems tailored to specific needs.
A comprehensive understanding of Photovoltaic system design is essential for maximizing energy efficiency in solar power installations.
Basics of Photovoltaic Systems
Photovoltaic technology is centered around converting sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. This technology has evolved significantly since its inception, making solar power one of the most preferred renewable energy sources today. By harnessing sunlight, photovoltaic systems play a crucial role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
A photovoltaic system primarily consists of three key components: solar panels, inverters, and a mounting system. Solar panels are made up of PV cells that generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. Inverters are responsible for converting the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses. The mounting system secures the solar panels in place and ensures they capture maximum sunlight throughout the day.
The working principle of photovoltaic cells involves the photovoltaic effect, where semiconductor materials (such as silicon) are exposed to sunlight, resulting in the release of electrons. This movement of electrons generates DC electricity. The electricity produced can either be used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed into the electrical grid, depending on the system's configuration.
System Design Principles
Sizing photovoltaic systems for residential use is a fundamental step in photovoltaic system design. Determining the right size involves analyzing the household's energy consumption patterns, expected energy savings, and available roof space for solar panel installation. Designers often use tools like solar calculators or software applications to estimate the size and energy production potential of the system.
Understanding the differences between grid-tied and off-grid photovoltaic systems is crucial for choosing the right design. Grid-tied systems are connected to the local electricity grid, allowing for seamless integration and utility interaction. In contrast, off-grid systems operate independently and require energy storage solutions like batteries to supply continuous power, making them ideal for remote locations without grid access.
Shading analysis is a critical aspect of system design. Properly assessing potential shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions ensures that solar panels receive adequate sunlight, maximizing energy production. Tools like shading analysis software can help visualize and evaluate potential shading effects throughout the year, ultimately influencing the positioning and orientation of solar panels.
Inverters in Photovoltaic Systems
Inverters are essential components of photovoltaic systems, with different types available for various applications. The most common inverter types include string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are typically used for larger systems, while microinverters are suited for situations where shading is a concern, as they maximize output from individual panels.
The primary role of inverters in energy conversion is to change the DC electricity generated by photovoltaic cells into usable AC electricity for homes and businesses. In addition, inverters often incorporate functions like monitoring system performance, providing safety disconnects, and ensuring compliance with grid requirements. The efficiency and reliability of inverters significantly influence the overall efficiency of the photovoltaic system.
Choosing the right inverter for your design involves considering factors such as compatibility with the solar panel configuration, monitoring capabilities, and warranties. Understanding the energy needs of the system and potential future expansions can further guide the selection process, ensuring that the inverter will perform optimally for the expected lifespan of the system.
Installation Best Practices
Site assessment is a critical step in the photovoltaic installation process. Factors such as roof condition, structural integrity, and solar access should be evaluated before design and installation begin. A thorough site assessment also identifies potential hazards and ensures compliance with local building codes and regulations.
Mounting techniques for solar panels vary depending on the type of roof or ground installation. Roof-mounted systems may use rack mounting systems, while ground-mounted panels often employ pole mounts or fixed tilts. Proper mounting ensures optimal exposure to sunlight and minimizes the risks of damage due to weather conditions, enabling maximum longevity and efficiency of the solar panels.
Safety measures during installation cannot be understated and include proper electrical practices, adherence to safety codes, and using protective equipment. Installer training and certifications play a vital role in ensuring the safety of the installation team and the effectiveness of the system being deployed.
Financial Considerations and Incentives
Conducting a cost analysis of photovoltaic system installation is essential for determining the budget and expected return on investment. This analysis should encompass not only the initial setup costs but also maintenance, operational costs, and financial incentives such as tax credits and rebates that can offset upfront expenses, making the system more financially viable.
Government incentives for solar energy projects often come in the form of tax credits, grants, and rebates at local, state, and federal levels. These programs can significantly improve the financial landscape of photovoltaic systems and help to stimulate solar energy adoption. Staying informed about available incentives can assist homeowners and businesses in maximizing their investment in solar technology.
Financing options for photovoltaic systems have expanded substantially. Numerous financial products are available, including solar loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs). These options allow system owners to reduce upfront costs and finance their systems over time, making solar energy accessible for a broader audience and promoting a sustainable energy future.
Future Trends in Photovoltaic Technology
Emerging technologies in photovoltaic cells are continuously reshaping the solar energy landscape. Innovations like bifacial solar panels, perovskite cells, and transparent photovoltaics promise increased efficiency and versatility in solar applications. Research and development in these technologies aim to make solar energy more competitive with traditional energy sources, thus accelerating adoption worldwide.
The impact of energy storage on system design is profound, as energy storage solutions are crucial for enhancing the reliability of photovoltaic systems. Integrating batteries with photovoltaic systems enables users to store excess energy generated during sunny days for use during periods of low generation, improving energy independence and self-consumption.
Integration of smart technology in photovoltaic systems presents exciting opportunities for enhanced performance monitoring, energy management, and automation. Smart inverters and monitoring systems enable real-time data analytics, resulting in optimized energy usage, predictive maintenance, and the potential for demand response measures that align energy consumption with grid requirements.
